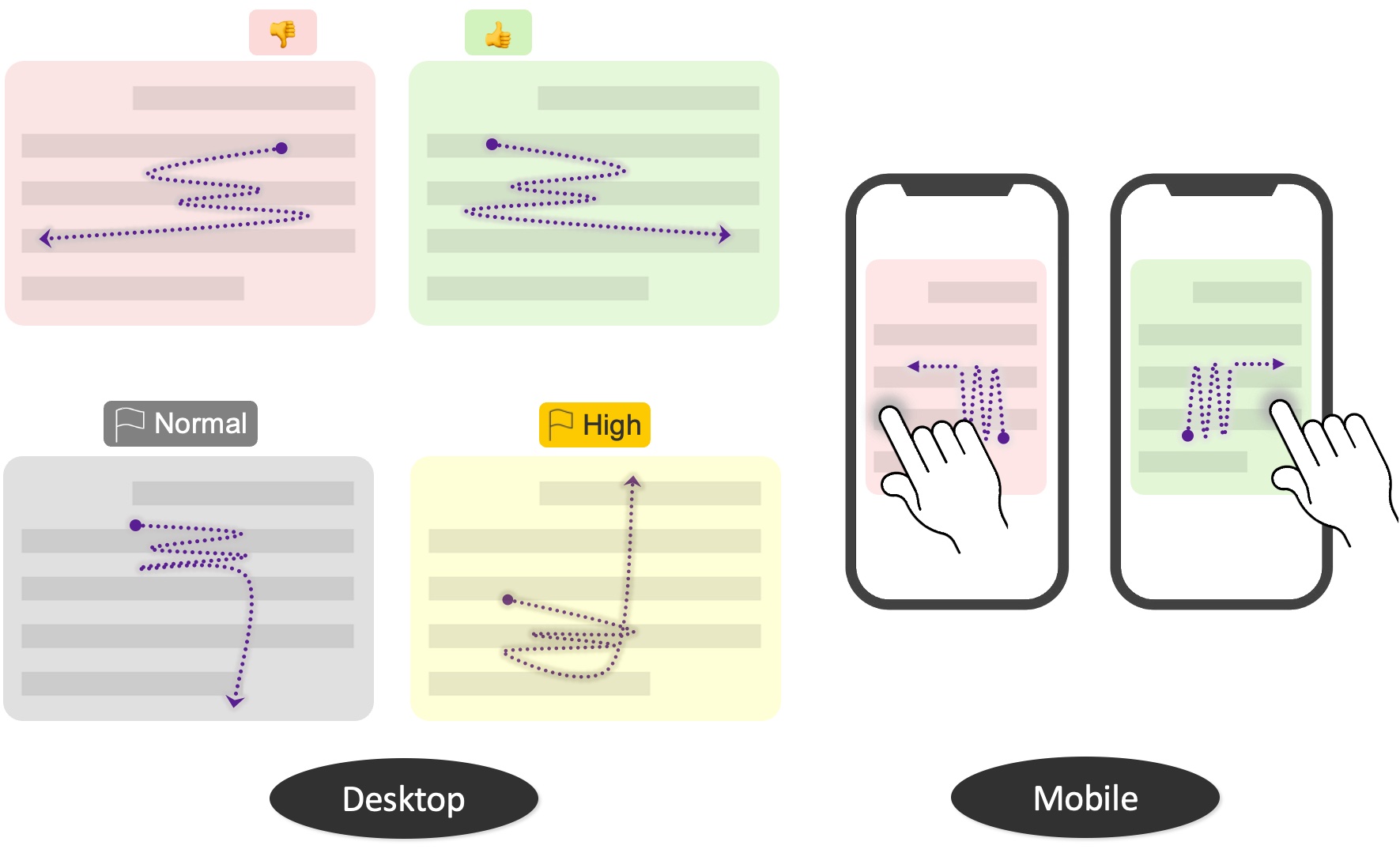
Users conducting online sensemaking tasks face the challenge of capturing the information they find for later use without interrupting their flow. Specifically, as people collect information, they also need to triaging support such as how urgent a topic is to follow up on, or rating a piece of evidence as a “pro” or “con,” which helps scaffold subsequent deeper exploration. However, current approaches incur a high cost, often requiring users to select, copy, context switch, paste, and annotate information. In this work, we explore a new interaction technique called “wiggling,” which can be used to fluidly collect, organize, and rate information during early sensemaking stages with a single gesture. Through implementation and user evaluation, we found that wiggling helped participants accurately collect information and encode their mental context with a 58% reduction in operational cost while being 24% faster compared to a common baseline.
Abstract
Consumers conducting comparison shopping, researchers making sense of competitive space, and developers looking for code snippets online all face the challenge of capturing the information they find for later use without interrupting their current flow. In addition, during many learning and exploration tasks, people need to externalize their mental context, such as estimating how urgent a topic is to follow up on, or rating a piece of evidence as a “pro” or “con,” which helps scaffold subsequent deeper exploration. However, current approaches incur a high cost, often requiring users to select, copy, context switch, paste, and annotate information in a separate document without offering specific affordances that capture their mental context. In this work, we explore a new interaction technique called “wiggling,” which can be used to fluidly collect, organize, and rate information during early sensemaking stages with a single gesture. Wiggling involves rapid back-and-forth movements of a pointer or up-and-down scrolling on a smartphone, which can indicate the information to be collected and its valence, using a single, light-weight gesture that does not interfere with other interactions that are already available. Through implementation and user evaluation, we found that wiggling helped participants accurately collect information and encode their mental context with a 58% reduction in operational cost while being 24% faster compared to a common baseline.
Downloads
Citation
1 2 3 | |
Bibtex
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |